|
Procedure
|
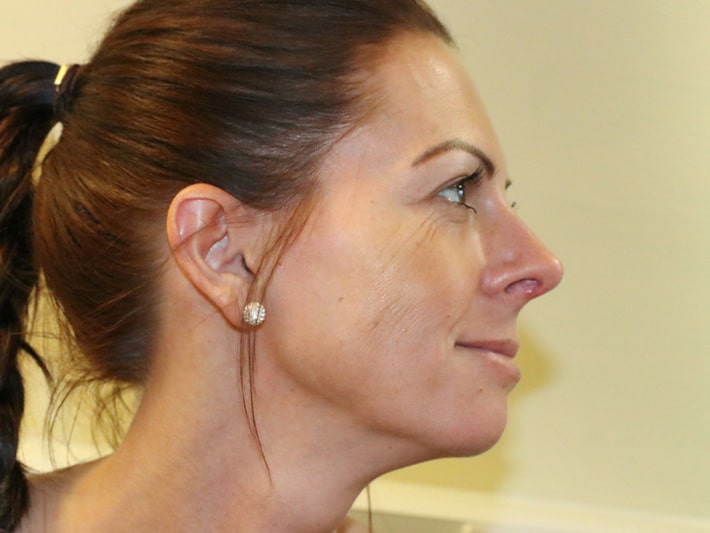
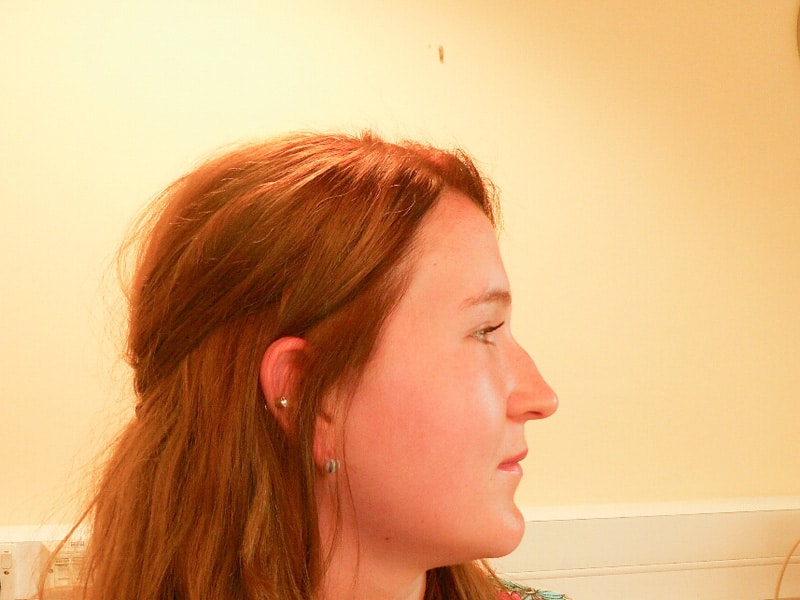
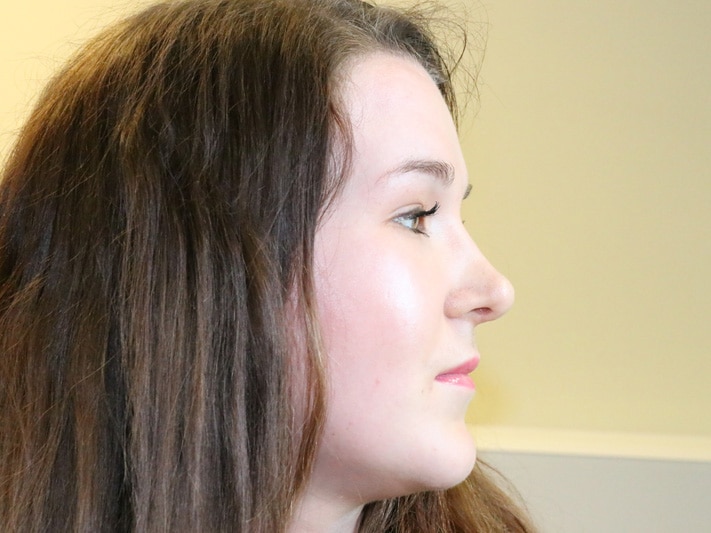
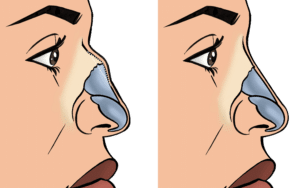
A rhinoplasty (=nose job) addresses perceived imperfections of the outer nose such as a hump on the bridge of the nose, a bulbous or droopy tip, asymmetry, flared or wide nostrils, a small (=underprojecting) or large (=overprojecting) nose and a low columella amongst others. A septoplasty reshapes the midline cartilage of the nose to improve breathing or appearance. A septorhinoplasty addresses aesthetic as well as functional issues. A small chin makes a nose look larger and vice versa. In some cases, chin alterations may be beneficial.
For functional problems such as breathing difficulty or frequent nose bleeds, an ENT opinion should be sought first.
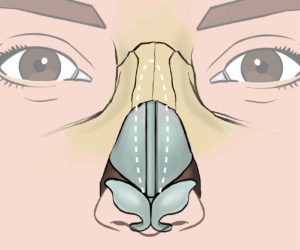
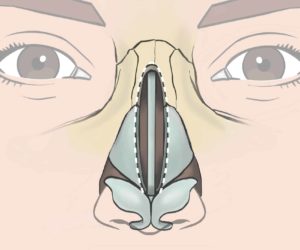
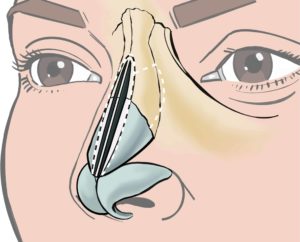
I prefer a closed rhinoplasty technique with scars inside the nostrils, but I might have to cut the columellar skin in between (=open rhinoplasty) for better surgical access.
After hump removal, the side walls of the bony bridge are cut (=infracture) with a chisel through small cuts in the skin to narrow the nose. Alternatively, a fine power tool (=piezotome) is used. The septal cartilage below is also reduced in height. The side cartilages (=upper lateral cartilages) can be fixed so that airflow is improved (=spreader flaps).
The tip is reshaped by cartilage trimming (=cephalic trim of the lower lateral cartilages), and with dissolving sutures to define the tip (=intradomal sutures) and to narrow it (=interdomal sutures).
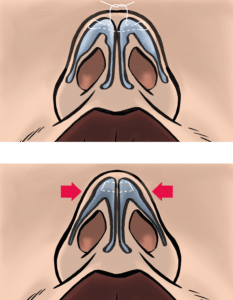
An alarplasty narrows the nostrils and / or reduces flaring. This involves additional scars at the sill and / or in the crease of the nostrils.
Cartilage grafts from the septum, ears or ribs can be used for structural support or augmentation (=enhancement). A softer graft can be taken from the superficial temporal fascia.
The sutures dissolve within six months and do not require removal. The nose is usually splinted for one week on the outside with a plastic splint and inside the nostrils with dissolving splints.
It can take up to three years to see the final shape. An enlarged tip after surgery is usually caused by swellling which responds to steroid injections, and by thickened skin, especially with a background of acne or rosacea. Dermatologists can often treat this. According to medical literature 5-20% of patients request further adjustments.
|
|
Scars
|
Within the nostrils (closed rhinoplasty) and chevron or “V”–shaped across the base (open rhinoplasty) and minute scars on the side of the nose. For nostril corrections (=alarplasty), the scars are in the outer creases (=alar creases) and / or in the sill of the nostril.
|
|
Operation time
|
2.5 hours
|
|
Anaesthesia
|
General for septum or bony surgery. Local for tip and nostrils
|
|
Hospital Stay
|
Day Surgery > (Overnight)
|
|
Benefits
|
Aesthetic, Psychological, Functional, Symptomatic
|
|
Risks
|
Bleeding, Infection, Scar problems (stretched, thick, abnormal pigmentation, red, retracted etc.), Necrosis, Thick skin, Skin discoloration, Wound separation, Slough, Pain, Nerve injury (Numbness), Non- animated nose, Bruising, Swelling, Overcorrection (e.g. saddle nose), Undercorrection, Polly beak deformity, Asymmetry, Inability to correct asymmetry, Aesthetic imperfections, With cartilage grafts: Graft failure & Donor morbidity of septum, ears, ribs [pneumothorax, mediastinitis]), Organ injury, Injury to tear duct / lining of skull, Loss of smell / taste, Breathing difficulty, Hump recurrence, Extrusion of bone / grafts / stitches, Septal perforation, Contour irregularities, Need for further surgery, Allergic reaction, Toxic Shock Syndrome, (General anaesthetic: Chest infection, Heart attack, Stroke, Blood clots in legs & lungs). N.B. Most complications are unlikely. Serious risks or death are rare
|
|
Risk factors
|
Alcohol, Asymmetry cannot be entirely corrected, Sneezing, Thick nasal skin or pre-existing skin conditions such as acne or rosacea limit refinements, Heavy glasses shortly after surgery, Previous surgery, Too early or excessive mobilisation, Wound interference without surgeon's agreement;
Contraindications which preclude surgery unless discussed otherwise in the consultation:
Smoking / vaping / nicotine / recreational inhalations within 6 weeks before and after surgery,
Contraception with estrogens or HRT tablets (if under general anaesthetic),
Air travel over 2 hours within 6 weeks before and after surgery (if under general anaesthetic),
Air travel under 2 hours within 2 weeks before and after surgery,
Overweight (Body Mass Index = BMI of 27 and over),
Recent weight changes over 6kg,
Pregnancy (if under general anaesthetic),
Raised blood pressure (if poorly controlled),
Bleeding tendency (Stop herbal products or supplements for two weeks before surgery),
Diabetes or immunosuppression (if poorly controlled)
|
|
Optimising factors
|
Diet rich in Vitamin C and protein, plenty of fluids, fresh air, sufficient sleep, manual lymphatic drainage, massage, nasal exercises and taping as directed by the surgeon, protection from sun and trauma; silicone gel for external scars only, dermatological input after surgery for thick skin
|
|
Discomfort
|
1 - 2 weeks
|
|
Bruising
|
2 - 3 weeks
|
|
Recovery
|
Light activities 2 weeks, Driving 1 - 2 weeks, Physical work and sports 6 weeks, Unrestricted 3 months
|
|
Acceptable appearance
|
3 - 8 weeks for most patients (This is subjective)
|
|
Final result
|
18 - 36 months
|
|
Alternatives
|
No Surgery, Make-up, Fillers
|