|
Procedure
|
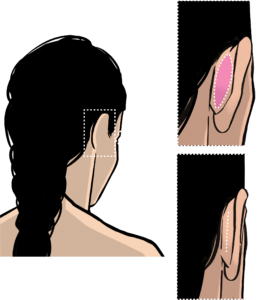
Ears can be reshaped with a procedure called pinnaplasty (=otoplasty / ear reduction / ear pinning / bat ear correction / prominent ear correction / sticking out ear correction). Prominent ears are caused by an underdeveloped ear fold (=antihelical fold) and by large mid-ears (=conchal bowls). They can cause aesthetic concerns and problems with headwear, helmets and headphones.
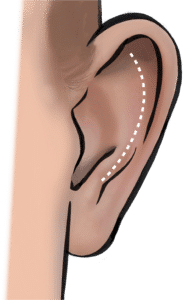
Ear folding is done through a cut in the crease behind the ear. The skin is elevated, and the cartilages are reshaped with cuts, cartilage removal and dissolving stitches.
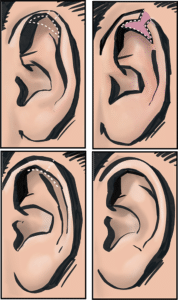
Some patients like to have their ear size reduced. This can be combined with a folding procedure. A "T"-shaped cut across the ear rim (=helix) which extends in the rim fold (=scaphoid fossa) is used.
The wounds are repaired with sutures under the skin which do not require removal and dissolve within four months. A head bandage has to be worn for a week afterwards and is then replaced with a head band to be worn at night or when engaging with sports.
|
|
Scars
|
In the crease behind the ear for protruding ears. Across and under rim for large ears.
|
|
Operation time
|
1.5 hours
|
|
Anaesthesia
|
Local
|
|
Hospital Stay
|
Day Surgery
|
|
Benefits
|
Aesthetic, Psychological, Functional
|
|
Risks
|
Bleeding, Infection, Scar problems (stretched, thick, abnormal pigmentation, red, retracted etc.), Skin discoloration, Skin cones, Wound separation, Slough, Necrosis, Pain, Numbness, Bruising, Swelling, Overcorrection, Undercorrection, Asymmetry, Recurrent prominence, Sharp / straight ear folds, Aesthetic imperfections, Functional problems, Contour irregularities, Need for further surgery, Allergic reaction.
N.B. Most complications are unlikely. Serious risks or death are rare
|
|
Risk factors
|
Smoking / high blood pressure, bleeding tendency (Stop herbal products or supplements for two weeks before surgery), diabetes
|
|
Optimising factors
|
Diet rich in Vitamin C and protein, plenty of fluids, fresh air, scar massage, sun protection, headband for 6-12 weeks
|
|
Discomfort
|
1 - 2 weeks
|
|
Bruising
|
2 - 3 weeks
|
|
Recovery
|
Light activities and driving one week, Physical work & sports 6 weeks, Unrestricted 3 months
|
|
Acceptable appearance
|
2 - 4 weeks for most patients (This is subjective)
|
|
Final result
|
6 - 18 months
|
|
Alternatives
|
No Surgery, Hair-styling, Ear-molding in young babies, Earfold device
|