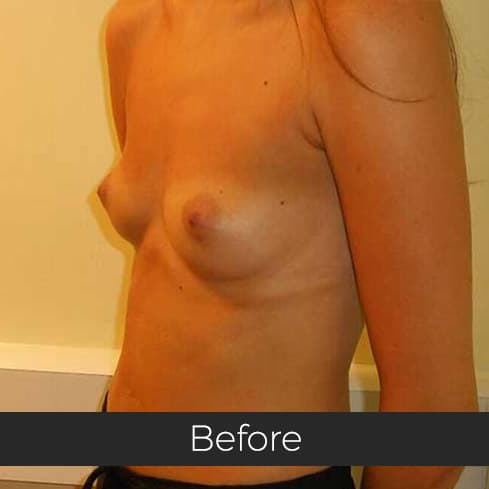
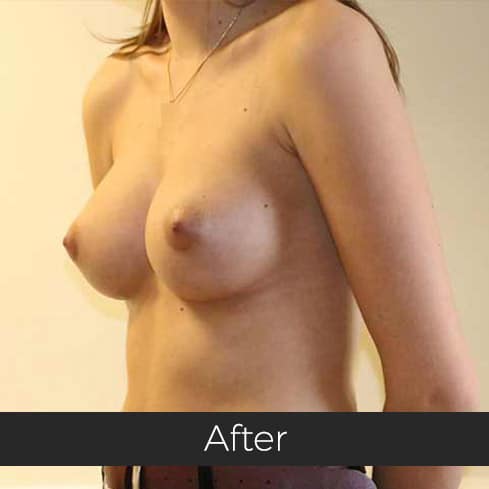
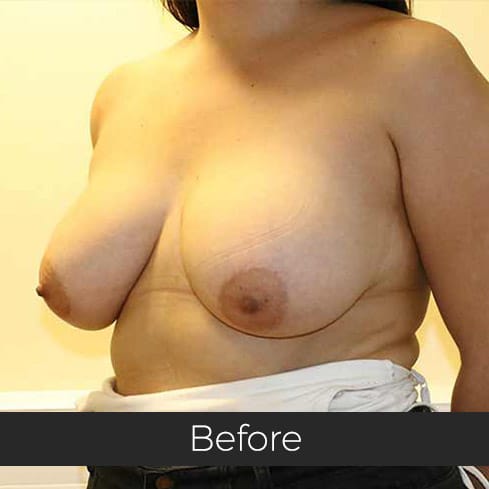
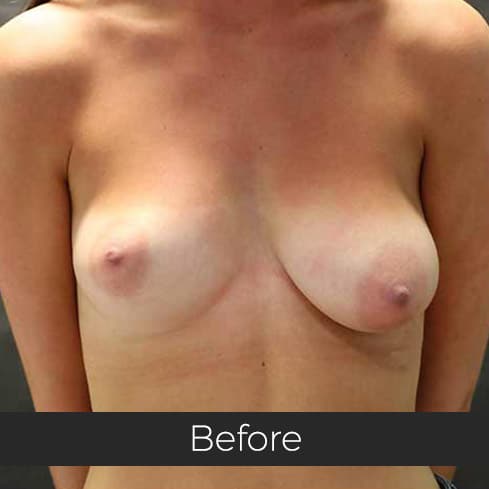
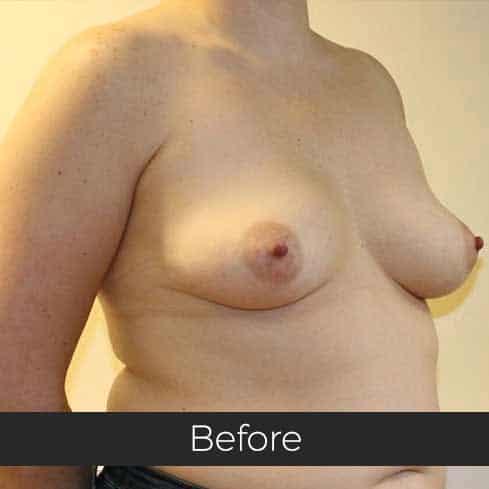
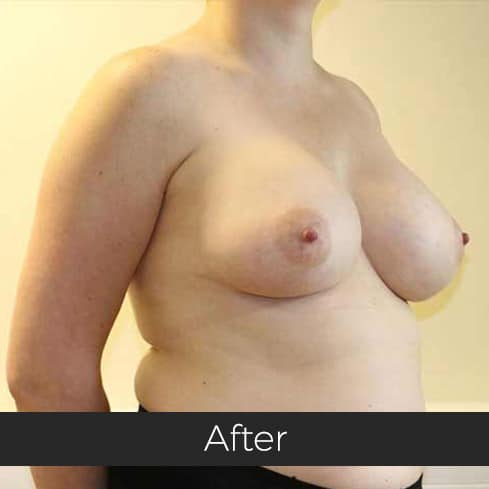
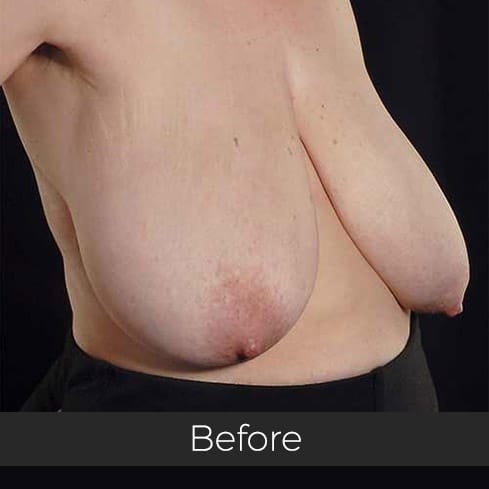
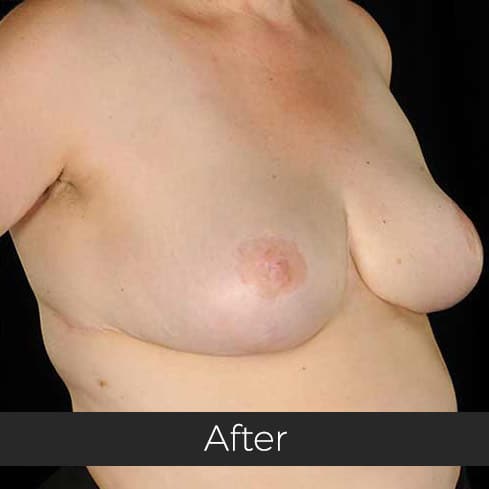
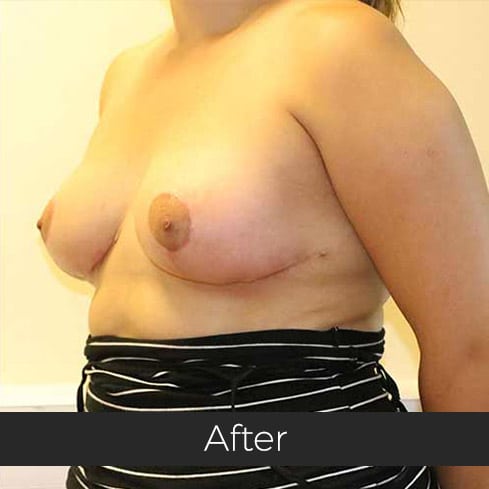
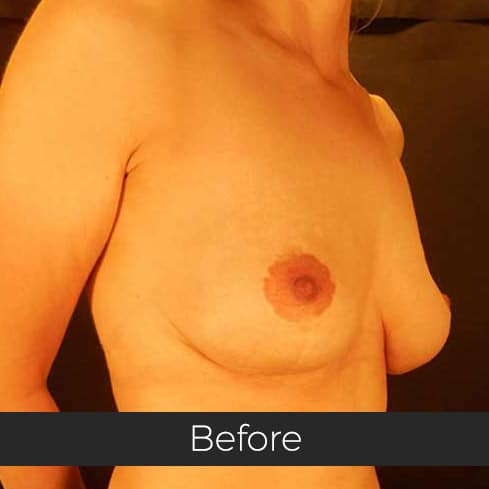
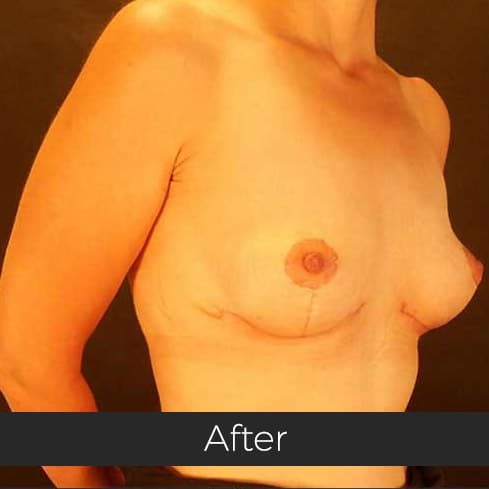
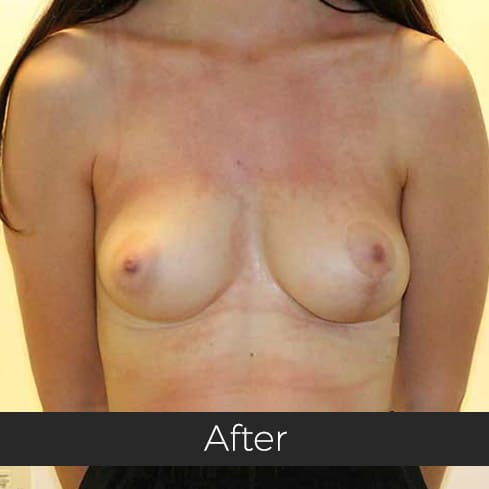
Gynecomastia (pronounced guy-ne-co-mastia) is a medical term meaning male breast enlargement. In the majority of cases there is no known cause and, although rarely talked about, it is a common condition. For men who feel self-conscious about their appearance, breast-reduction surgery can be helpful. The procedure removes tissue from the breasts, and in extreme cases excess skin. This information sheet will give you a basic understanding of what is involved if you are considering surgery to correct gynecomastia. It can’t answer all of your questions, as a lot depends on your personal situation.
Most teenage boys experience some degree of breast enlargement affecting one or both breasts. However, by early adulthood less than 10% have a residual problem. This incidence rises with age, reaching approximately 30% (1 in 3) in older men. Rarely, the breast enlargement can be caused by medicines (for high blood pressure, heart disease and prostate cancer), drugs (such as marijuana and anabolic steroids), some diseases (such as liver failure and some cancers) and some very rare congenital abnormalities (errors of development that one is born with). These causes should be excluded by the surgeon during an initial consultation. Additional information will be needed at this consultation regarding overall health, chest size and body shape, previous chest surgery, any bleeding tendencies and healing capabilities, some of which will be affected by smoking, alcohol and various medications.
You can find more information regarding the procedure on the BAAPS website.